Chapter 10
Chapter 10 Slides(pptx)
Errata
Last updated 2019-10-08
- p. 161. In Example 10.1, lines 4 and 5, there was a factor of pi missing in the argument of the sinc functions.
- p. 163. In marginal note 5 there was an extraneous parenthesis at end.
- p. 166. 4 lines in Fourier transform needed a factor of two before the delta(u), and to be divided by 4, not 2.
Exercises
- (10.7). There was a missing] to close the hint at the end of the question.
Extras
Spatial filtering simulation
Topics: 4f spatial filer, high- and low- pass
This code was used to create Fig. 10.7 on p. 166 in Optics f2f. The simulation uses the same angular spectrum code that we introduced in Chapter 6, see also Chapter 6 Extras, imprints a quadratic phase to simulate the lenses, and applies a blocking filter in the ‘Fourier plane’.
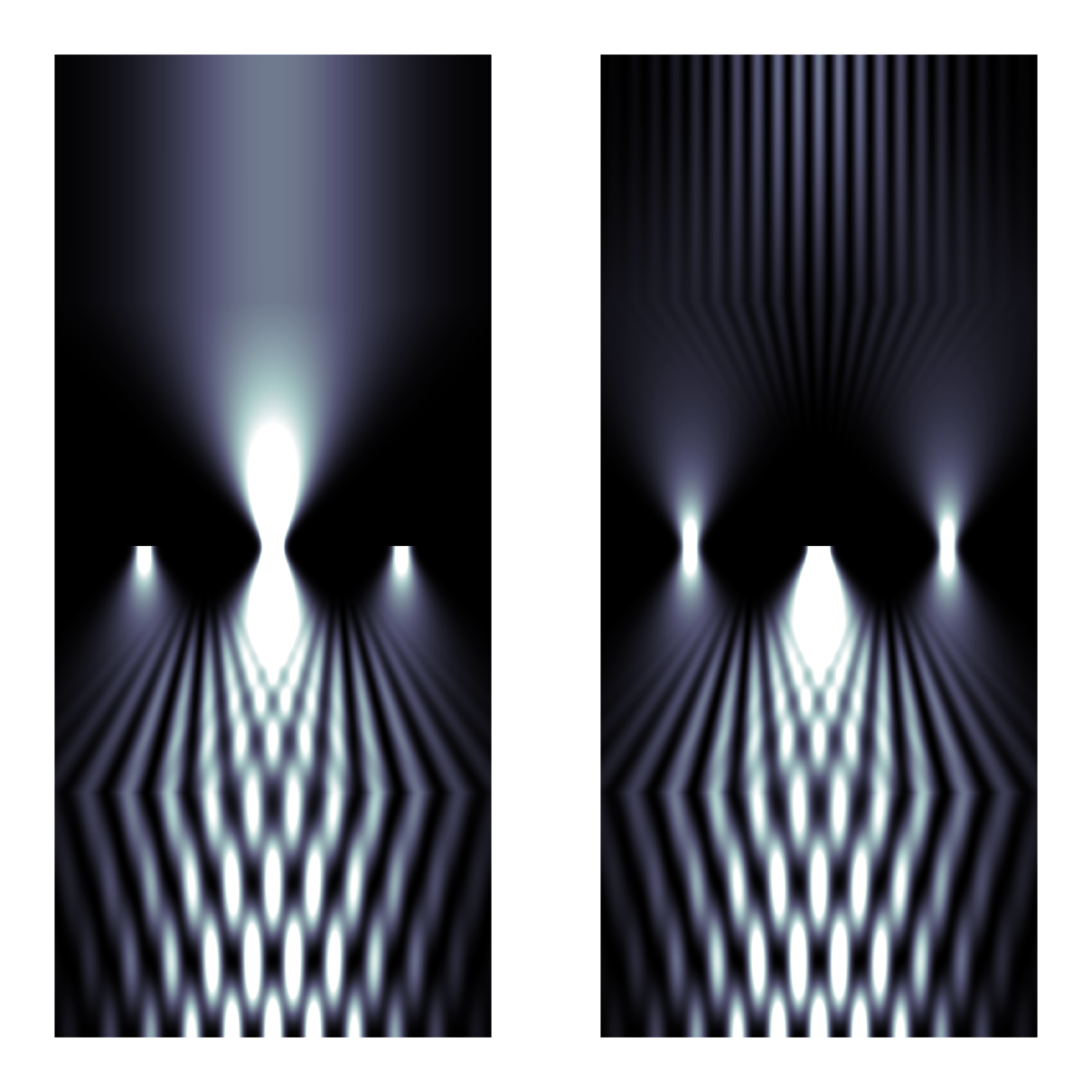
Figure 1: The intensity distribution in the xz plane (z is vertical in this plot) for light propagating through a 4f spatial filter. The left and right plots show examples of low and high-pass filtering, respectively. Fig. 10.7 on p. 166 in Optics f2f has the lenses and filter added.
Spatial filtering: 2D transverse dimensions
Topics: 4f spatial filer, high- and low- pass
The previous example illustrated spatial filtering in one transverse dimension only. In this code we explore filtering in both x and y. A variant of this code was used to create Fig. 10.8 on p. 167 in Optics f2f. In this code we only calculate the field in the Fourier and the output planes.
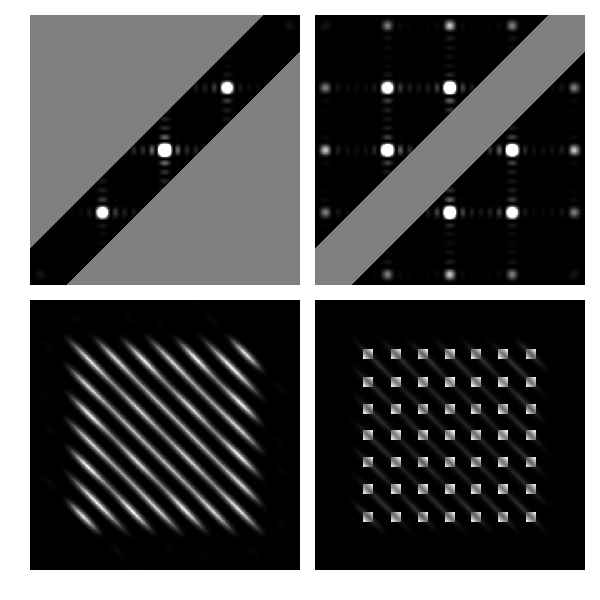
Figure 1: Low- and high-pass filtering of an array. The top row shows the intensity distribution in the Fourier plane together with the mask. The bottom row shows the field in the output plane.
The code is quite flexible. For example, if we put wy=wx to produce a circular aperture in the Fourier plane we obtain.
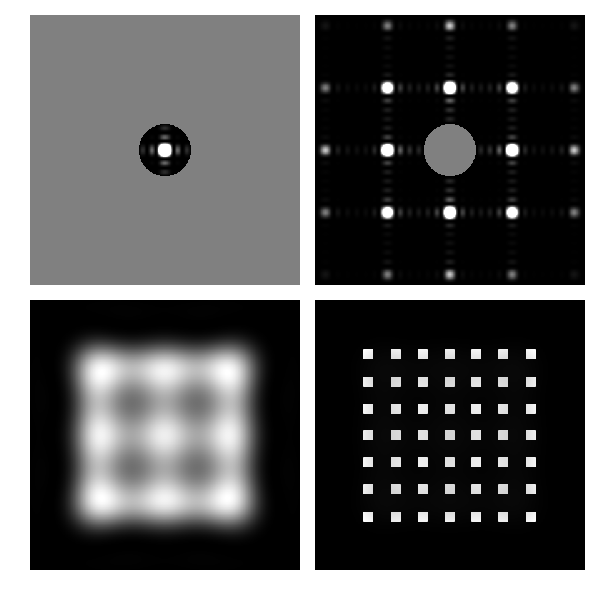
Figure 2: Low- and high-pass filtering of an array. The top row shows the intensity distribution in the Fourier plane together with the mask. The bottom row shows the field in the output plane.
